
Let’s iterate over a range of values 1 to 5. Once we create a range, we can iterate over it using the for (x in. The second call confirms that the value “helq” is not in the range.
The first call verifies that the range includes the value “helm”, which is in the lexical order of words between the values “hell” and “help”. println(ntains("helm")) //true println(ntains("helq")) //false Let’s quickly check if a couple of values exist in that range. The range includes both the values before and after the. operator, followed by the last value in the range. Here’s a range of strings: val seekHelp: ClosedRange = "hell"."help" You’re not limited to primitives like int, long, and char. If you want a range of letters in the English alphabet, the process is the same: val aToE: CharRange = 'a'.'e' The type IntRange, which is part of the kotlin.ranges package, is provided for clarity, but you may leave it out and let type inference figure out the variable’s type.

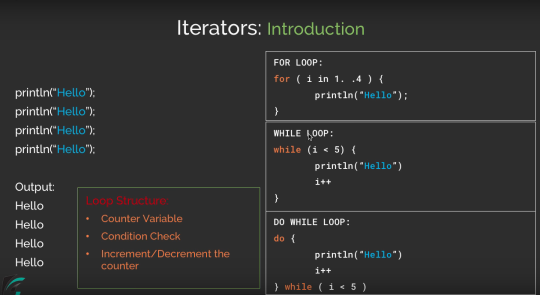
For instance, here’s a way to create a range of numbers from 1 to 5. Kotlin raises the level of abstraction to iterate over a range of values with specialized classes. But we don’t have to, at least not in Kotlin. Yet that’s how programmers have been writing code in many C-like languages. Imagine telling someone to count from one to five by uttering “set i equal to 1 but while keeping i less than 6, increment i and report the value.” If we had to communicate with a fellow human that way, it would have ended civilization a long time ago. In this blog, we are going to learn about ranges and iteration in kotlin.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
